PlotlyChart
Displays a Plotly chart.
Warning
This control requires the plotly Python
package to be installed.
See this installation guide for more information.
Inherits: Container
Properties
-
figure(Figure) –Plotly figure to draw.
-
original_size(bool) –Whether to display this chart in original size.
Examples#
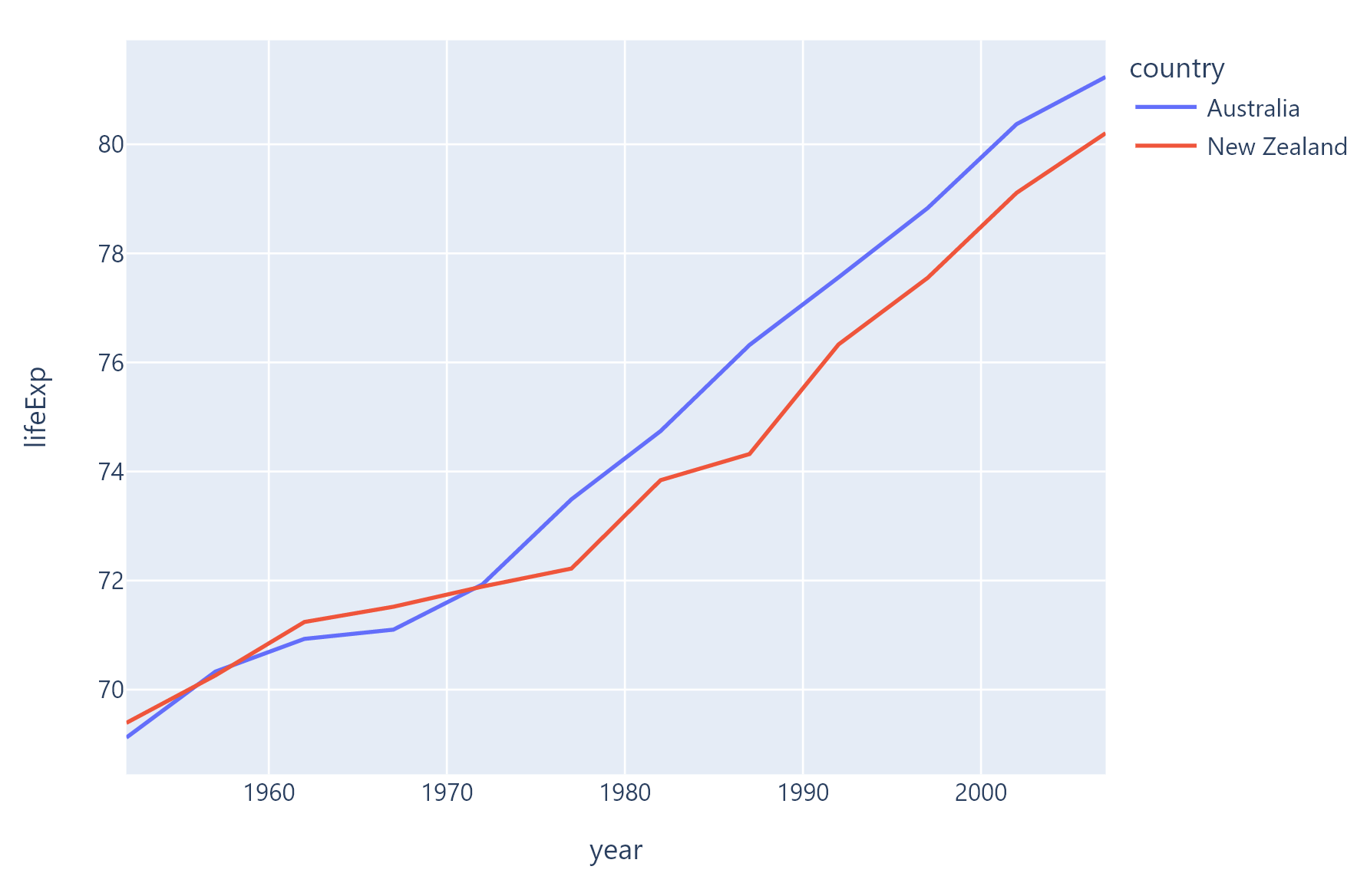
Example 1#
Based on an official Plotly example.
import flet as ft
import plotly.express as px
import flet_charts as fch
def main(page: ft.Page):
df = px.data.gapminder().query("continent=='Oceania'")
fig = px.line(df, x="year", y="lifeExp", color="country")
page.add(fch.PlotlyChart(figure=fig, expand=True))
ft.run(main)
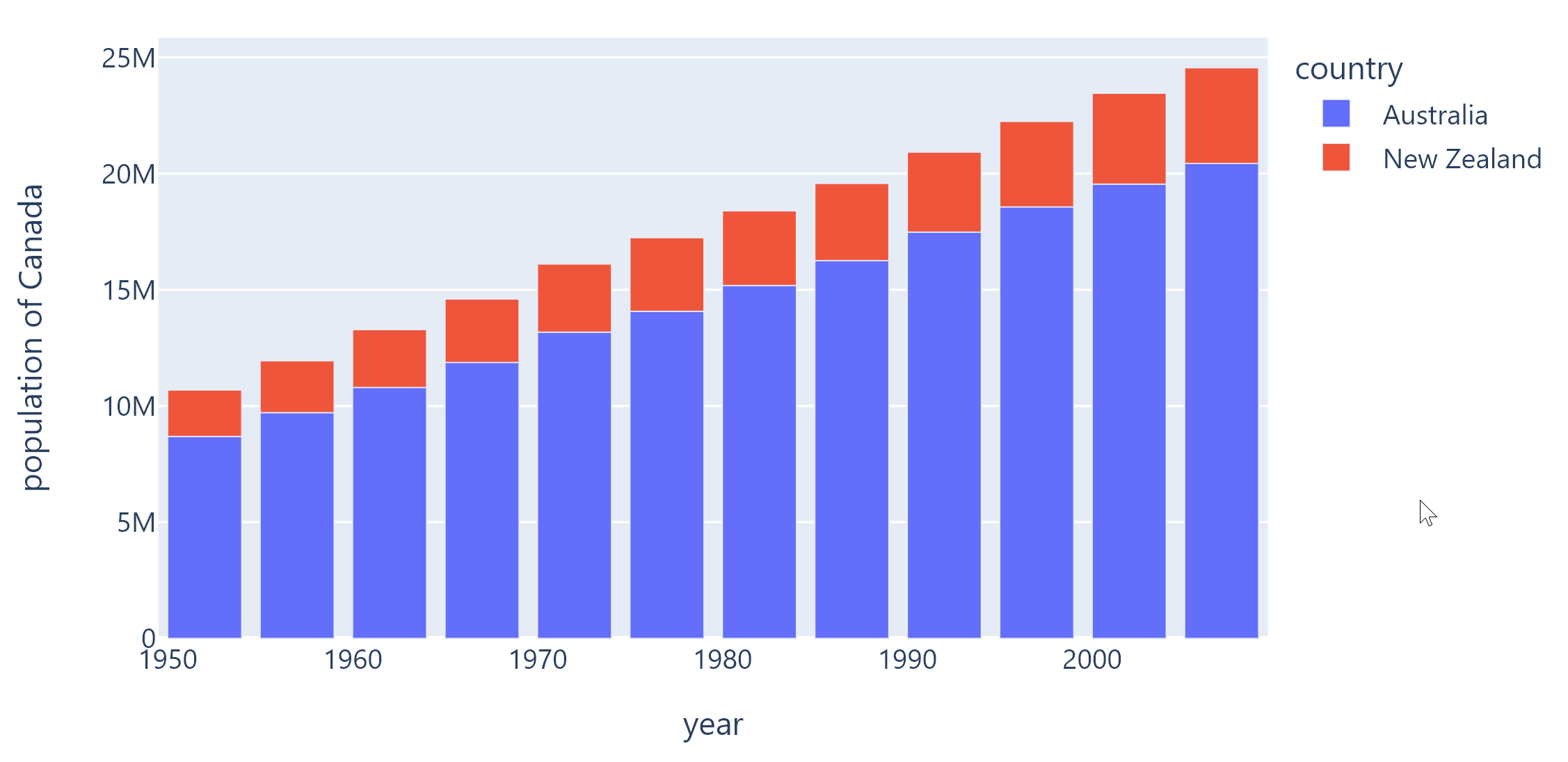
Example 2#
Based on an official Plotly example.
import flet as ft
import plotly.express as px
import flet_charts as fch
def main(page: ft.Page):
df = px.data.gapminder().query("continent == 'Oceania'")
fig = px.bar(
df,
x="year",
y="pop",
hover_data=["lifeExp", "gdpPercap"],
color="country",
labels={"pop": "population of Canada"},
height=400,
)
page.add(fch.PlotlyChart(figure=fig, expand=True))
ft.run(main)
Example 3#
Based on an official Plotly example.
import flet as ft
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import flet_charts as fch
def main(page: ft.Page):
labels = ["Oxygen", "Hydrogen", "Carbon_Dioxide", "Nitrogen"]
values = [4500, 2500, 1053, 500]
fig = go.Figure(data=[go.Pie(labels=labels, values=values)])
page.add(fch.PlotlyChart(figure=fig, expand=True))
ft.run(main)
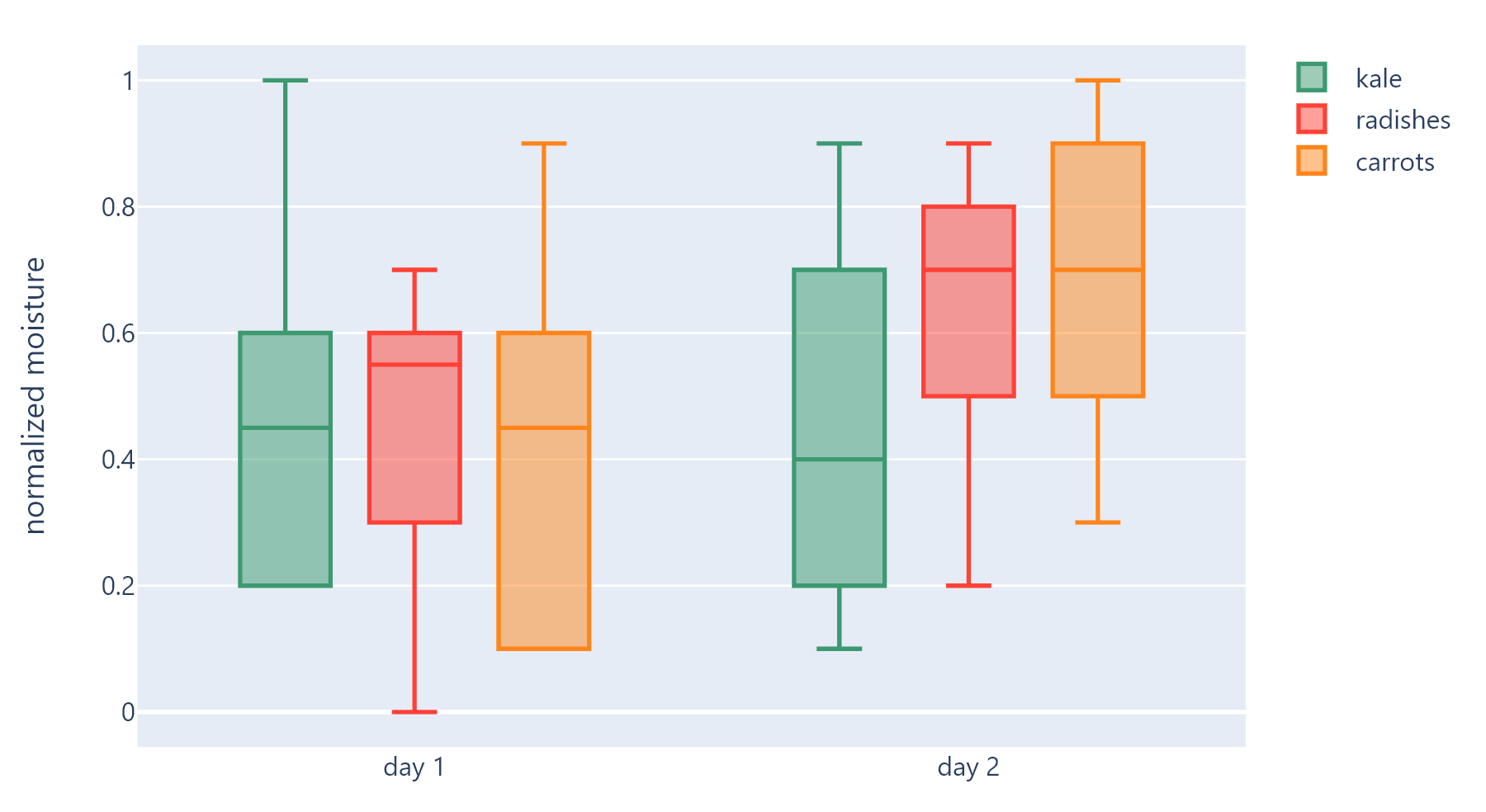
Example 4#
Based on an official Plotly example.
import flet as ft
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import flet_charts as fch
def main(page: ft.Page):
x = [
"day 1",
"day 1",
"day 1",
"day 1",
"day 1",
"day 1",
"day 2",
"day 2",
"day 2",
"day 2",
"day 2",
"day 2",
]
fig = go.Figure()
fig.add_trace(
go.Box(
y=[0.2, 0.2, 0.6, 1.0, 0.5, 0.4, 0.2, 0.7, 0.9, 0.1, 0.5, 0.3],
x=x,
name="kale",
marker_color="#3D9970",
)
)
fig.add_trace(
go.Box(
y=[0.6, 0.7, 0.3, 0.6, 0.0, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9, 0.5, 0.8, 0.7, 0.2],
x=x,
name="radishes",
marker_color="#FF4136",
)
)
fig.add_trace(
go.Box(
y=[0.1, 0.3, 0.1, 0.9, 0.6, 0.6, 0.9, 1.0, 0.3, 0.6, 0.8, 0.5],
x=x,
name="carrots",
marker_color="#FF851B",
)
)
fig.update_layout(
yaxis_title="normalized moisture",
boxmode="group", # group together boxes of the different traces for each value of x
)
page.add(fch.PlotlyChart(figure=fig, expand=True))
ft.run(main)